The anticipation and excitement that come with the news of expecting a baby are unparalleled. From the moment a mother first discovers that tiny bump forming, a world of emotions and experiences awaits her. Throughout the journey, from the baby’s initial movements, growing kicks, and hiccups, to the eventual arrival of the little one, a mother goes through a whirlwind of emotions. It is a time of immense joy, nervousness, wonder, and even a few challenges along the way.
In this article, we will delve into the emotions and experiences a mother encounters during the period from the baby’s bump until the moment of birth. We will explore the unique bond that develops, the physical changes experienced, the dreams and hopes that shape a mother’s journey and the profound love that blossoms as she awaits the arrival of her precious bundle of joy. Join us as we dive into the incredible journey of a mother from the baby’s bum to the wondrous moment when her baby enters the world.
Week-by-Week Stages of Pregnancy
Understanding the week-by-week stages of pregnancy can provide expectant parents with valuable insights into the remarkable changes happening within, as well as the milestones their baby is reaching along the way.
Weeks 1-5: Fertilization occurs in the first week, leading to the formation of a cluster of cells called a zygote. By the second week, implantation into the uterine lining takes place. In the third week, the neural tube and major blood vessels start to develop. By the fourth week, facial features and limb buds begin to form, and the heart starts beating. In the fifth week, the embryo’s brain, spinal cord, and circulatory system continue to develop.
Weeks 6-10: By the sixth week, facial features become more distinct, and the embryo’s heart is fully developed and beating regularly. In the seventh week, the arms and legs elongate, and fingers and toes start to form. By the eighth week, the embryo transforms into a fetus, with all major organs formed, and it begins to make small movements. In the ninth week, the fetus develops tooth buds and differentiated external genitalia. By the tenth week, the fetus’s vital organs are fully formed, and it can make reflexive movements and swallow amniotic fluid.
Weeks 11-15: During the eleventh week, the fetus undergoes rapid growth, developing fine hair called lanugo and more distinct facial features. In the twelfth week, the ears reach their final position, and the fetus can make sucking motions. By the thirteenth week, the fetus grows to about 3 inches and starts developing vocal cords. In the fourteenth week, the fetus’s neck elongates, and it can produce urine. By the fifteenth week, the fetus grows to about 4 inches, with freely moving limbs and more opaque skin.
Weeks 16-20: During the sixteenth week, the fetus experiences a growth spurt, its body becomes more proportionate, and vernix caseosa begins forming. In the seventeenth week, the fetus can hear outside sounds. By the eighteenth week, the fetus’s fingerprints and footprints develop. In the nineteenth week, the fetus starts to experience quickening, which is the first fetal movement felt by the mother. By the twentieth week, the fetus reaches about 6 inches and begins to develop a protective coating called lanugo.
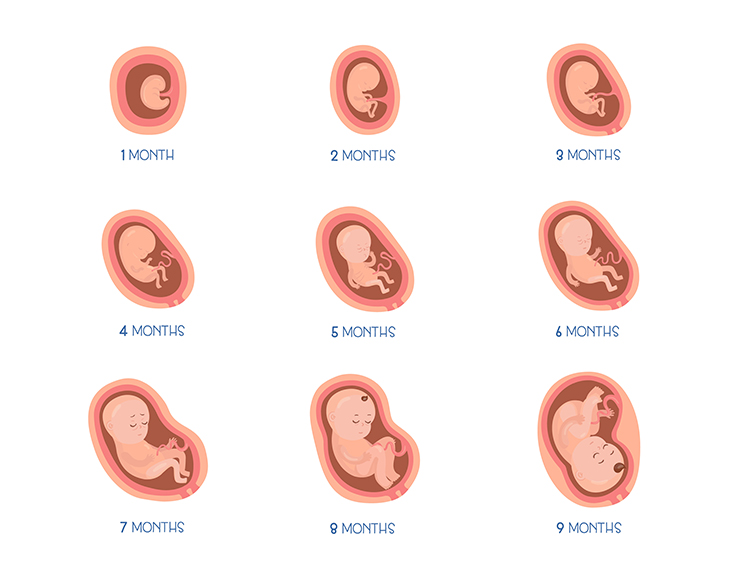
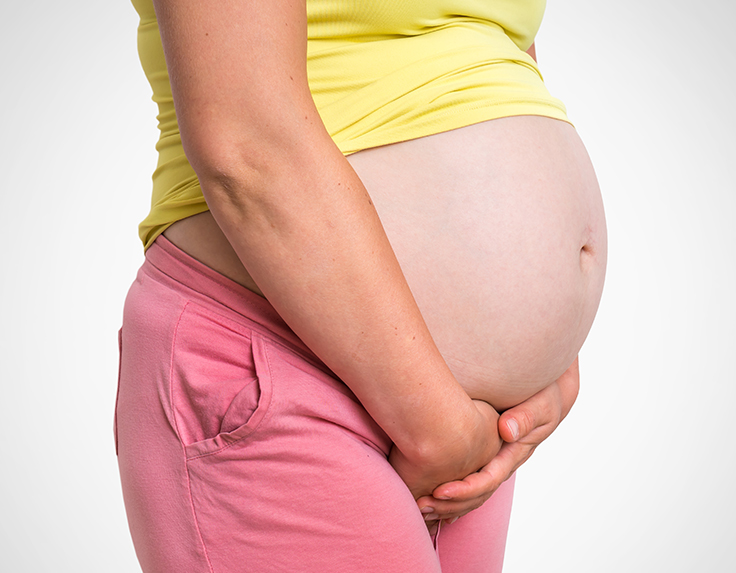
Body changes with the baby bump
As pregnancy progresses, the body undergoes various changes to accommodate the growing baby bump:
First Trimester: During the initial three months, hormonal changes may cause some women to experience breast tenderness, slight weight gain, and a bloated feeling. However, the baby bump itself is not usually prominent during this stage.
Second Trimester: This is when the baby bump becomes more noticeable. The uterus expands and rises above the pelvic bone, resulting in a visible protrusion in the lower abdomen. The belly gradually becomes rounder as the weeks go by. Some women may also experience skin changes, such as darkening of the linea nigra (a vertical line on the belly) and the appearance of stretch marks.
Third Trimester: The baby bump continues to grow in size and becomes larger and lower as the due date approaches. The skin around the abdomen may feel stretched and itchy due to the expanding belly. Many women also experience increased backache and discomfort as the weight of the baby increases.
Overall, the body undergoes significant changes to accommodate the developing baby, and each woman’s experience may vary. It’s important to embrace and care for your changing body throughout the pregnancy journey.
Stages of baby bump growth during pregnancy
During pregnancy, one of the most visible and exciting changes is the growth of the baby bump. As the precious little one develops and thrives inside the womb, the mother’s body goes through a series of remarkable transformations.
First Trimester: During the first three months, the baby is still small, and the bump may not be very noticeable. It is common to have a slight thickening around the waistline due to bloating and hormonal changes.
Second Trimester: This is when the baby bump becomes more prominent. Around weeks 12 to 16, the uterus rises above the pelvic bone, and the belly starts to round out. The bump gradually grows in size as the baby continues to develop. By the end of the second trimester, typically around 20 to 24 weeks, the bump is usually well-defined and visible.
Third Trimester: In the final three months, the baby bump becomes larger and more pronounced. It continues to grow as the baby gains weight and the uterus expands. Around the 28th week, the bump may start to feel heavier and lower as the baby settles into a head-down position. As the due date approaches, the bump may be quite large and may feel tight and stretched.
Every pregnancy is unique, and the size and shape of the baby bump can vary among women. Factors such as the position of the baby, the mother’s body type, and the number of pregnancies can all influence the appearance of the bump. It’s important to remember that the size of the bump is not necessarily an indication of the baby’s health or the progress of the pregnancy.
Now that we have set the stage for the stages of baby bump growth during pregnancy, let’s address some frequently asked questions that often arise regarding this fascinating aspect of the journey to motherhood.
Q1. When Do You Start Showing in Pregnancy?
The timing of when you start showing during pregnancy can vary. Typically, first-time mothers may start showing between 12 to 16 weeks, while women who have been pregnant before may show earlier, around 8 to 12 weeks. However, various factors like body type, muscle tone, and the position of the baby can influence when the baby’s bump becomes noticeable.
Q2. When Will My Pregnancy Start to Show?
Each woman’s body is unique, and the timing of when your pregnancy will start to show can differ. On average, most women begin to show signs of a baby bump during the second trimester, around 12 to 16 weeks. However, it’s essential to remember that every pregnancy is different, and some women may show up earlier or later.
Q3. What are the different stages of pregnancy?
Pregnancy is typically divided into three trimesters. The first trimester spans from week 1 to week 12, the second trimester encompasses week 13 to week 27, and the third trimester covers week 28 until birth. These stages mark significant developmental milestones for the baby and bring various physical and emotional changes for the mother.